学位論文要旨
| No | 114563 | |
| 著者(漢字) | 奥井,伸雄 | |
| 著者(英字) | ||
| 著者(カナ) | オクイ,ノブオ | |
| 標題(和) | HIV-1インテグレースに対する連鎖抗体を、Vprを介してウイルス粒子に取り込ませることによる感染力抑制 | |
| 標題(洋) | ||
| 報告番号 | 114563 | |
| 報告番号 | 甲14563 | |
| 学位授与日 | 1999.03.29 | |
| 学位種別 | 課程博士 | |
| 学位種類 | 博士(医学) | |
| 学位記番号 | 博医第1483号 | |
| 研究科 | 医学系研究科 | |
| 専攻 | 外科学専攻 | |
| 論文審査委員 | ||
| 内容要旨 | (背景と意義)HIV-1粒子が形成される際に抗ウイルス効果のある分子を取り込ませる方法による新しい遺伝子治療戦略をCTVI(capsid-targeted virion inactivation)という。CTVIは、放出されるウイルスを標的とする点で、感染細胞や細胞内でのウイルス複製を標的とした従来の遺伝子治療と異なる。本研究は、CTVIに有用な分子を開発することを目的とする。(材料と方法)抗HIV-1インテグレース単鎖抗体Single-Chain Antibody(scAb2-19)を作製した。scAb2-19の発現した細胞から放出されるHIV-1の粒子にscAb2-19は取り込まれない。このため、ウイルス粒子によく取り込まれる蛋白質であるHIV-1のViral protein R(Vpr)とscAb2-19を融合させたscAbE-Vpr*を発現するプラスミドの他、scAb2-19に核移行シグナルNLSをつけたscAb-NLS、パピローマウイルスE7に対する単鎖抗体とVprを付けたE7E-Vpr*を発現するプラスミドを作製した。ヒト293T細胞に、HIV-1 infectious clone pLAIと、Vpr*発現DNA、scAb発現DNA、scAbNLS発現DNA、scAbE-Vpr*発現DNA、E7E-Vpr*発現DNAをco-transfectionし、それぞれの細胞から産生したウイルス、HIV-1wild type、Vpr*-virus、scAb2-19-virus、scAbNLS-virus、scAbE-Vpr*-virus、E7E-Vpr*-virusを回収した。各ウイルス量は、p24 assayとRT assayで測定し、感染力は、MAGI assayで測定した。各ウイルスの蛋白質はイムノブロットにて解析した。Vpr*-virus、scAbE-Vpr*-virusを感染させたCEM細胞中のHIV-1cDNAをPCR法を用いて検出した。(結果)ウイルスの産生量には、大きな違いはなかった(Fig.1)。scAbE-Vpr*-virusの感染力は、完全に消失していたのに対して、scAb2-19-virusの感染力は、wild typeの1%程度であった(Fig.2)。各ウイルス中のインテグレースの量は同じであった(Fig.3)。scAbE-Vpr*-virusの粒子中にscAbE-Vpr*はVpr*と同程度に取り込まれていたのに対して、scAb2-19-virus中にscAb2-19はほとんど取り込まれていなかった(Fig.3)。scAbE-Vpr*-virus感染後4時間目からHIV-1cDNAが検出された。(考察)以上の結果より、scAbE-Vpr*は、高効率にウイルス粒子に取り込まれるため、大量のscAbE-Vpr*がウイルス粒子内のインテグレースに作用して、感染後の逆転写されたウイルスcDNAの組み込みを阻害し、ウイルスの感染力を抑制したものと思われる。scAbE-Vpr*は、ウイルス特有の酵素に対する単鎖抗体なので、宿主細胞に対して毒性はなく、効果的なCTVI用分子の開発ができた。 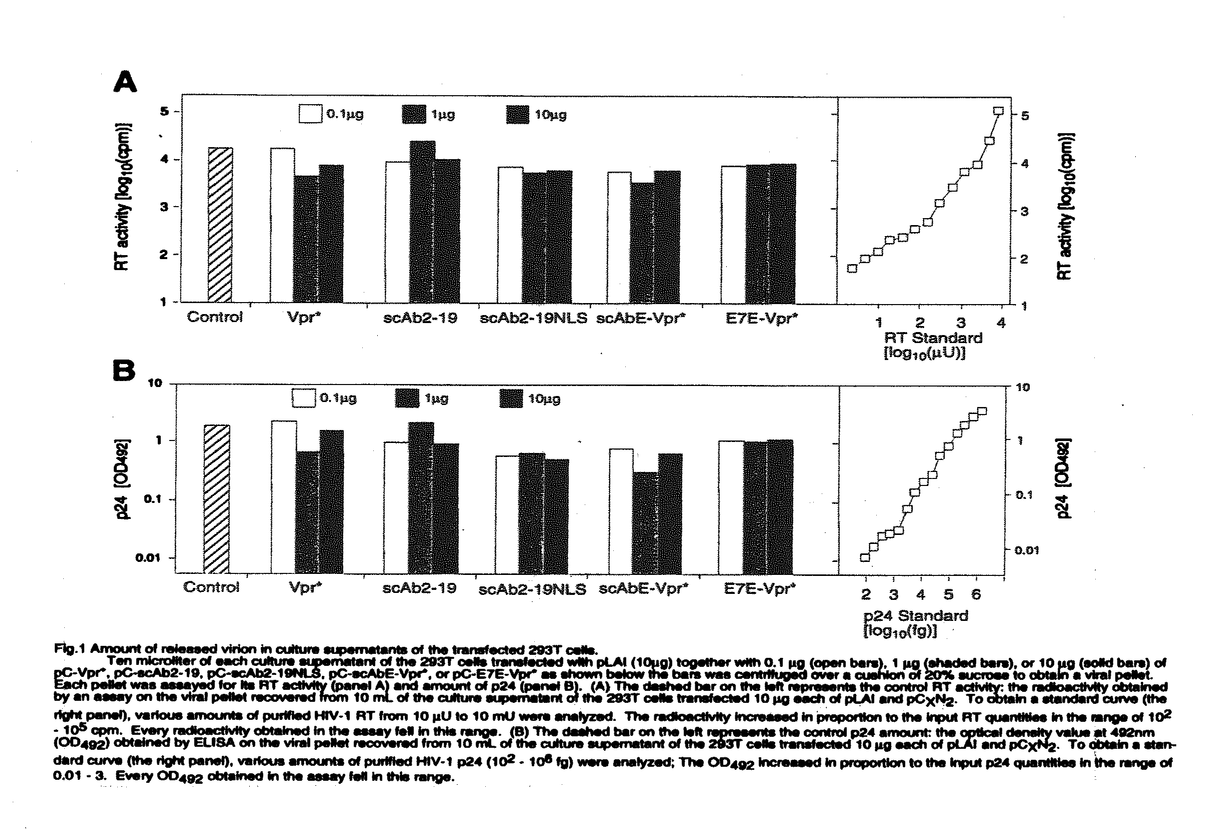 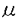 g)together with 0.1 g)together with 0.1 g(open bars),1 g(open bars),1 g(shaded bars),or 10 g(shaded bars),or 10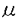 g (solid bars)of pC-Vpr*,pC-scAb2-19,pC-scAb2-19NLS,pC-scAbE-Vpr*or pC-E7E-Vpr*as shown below the bars was centrifuged over a cushion of 20% sucrose to obtain a viral pellet.Each pellet was assayed for its RT activity(panel A)and amount of p24(panel B).(A)The dashed bar on the left represents the control RT activity:the radioactivity obtained by an assay on the viral pellet recovered from 10mL of the culture supernatant of the 293T cells transfected 10 g (solid bars)of pC-Vpr*,pC-scAb2-19,pC-scAb2-19NLS,pC-scAbE-Vpr*or pC-E7E-Vpr*as shown below the bars was centrifuged over a cushion of 20% sucrose to obtain a viral pellet.Each pellet was assayed for its RT activity(panel A)and amount of p24(panel B).(A)The dashed bar on the left represents the control RT activity:the radioactivity obtained by an assay on the viral pellet recovered from 10mL of the culture supernatant of the 293T cells transfected 10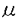 g each of pLAI and pCXN2.To obtain a standard curve (the right panel),various amounts of purified HIV-1 RT from 10 g each of pLAI and pCXN2.To obtain a standard curve (the right panel),various amounts of purified HIV-1 RT from 10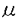 U to 10mU were analyzed.The radioactivity increased in proportion to the input RT quantities in range of 102-105cpm.Every radioactivity obtained in the assay fell in this range.(B)The dashed bar on the left represents the control p24 amount:the optical density value at 492nm (OD492)obtained by ELISA on the viral pellet recovered from 10mL of the culture supernatant of the 293T cells transfected 10 U to 10mU were analyzed.The radioactivity increased in proportion to the input RT quantities in range of 102-105cpm.Every radioactivity obtained in the assay fell in this range.(B)The dashed bar on the left represents the control p24 amount:the optical density value at 492nm (OD492)obtained by ELISA on the viral pellet recovered from 10mL of the culture supernatant of the 293T cells transfected 10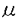 g each of pLAI and pCXN2.To obtain a standard curve (the right panel), various amounts of purified HIV-1 p24 (102-106fg) were analyzed; The OD492 increased in proportion to the input p24 quantities in the range of 0.01-3.Every OD492obtained in the assay fell in this range. g each of pLAI and pCXN2.To obtain a standard curve (the right panel), various amounts of purified HIV-1 p24 (102-106fg) were analyzed; The OD492 increased in proportion to the input p24 quantities in the range of 0.01-3.Every OD492obtained in the assay fell in this range.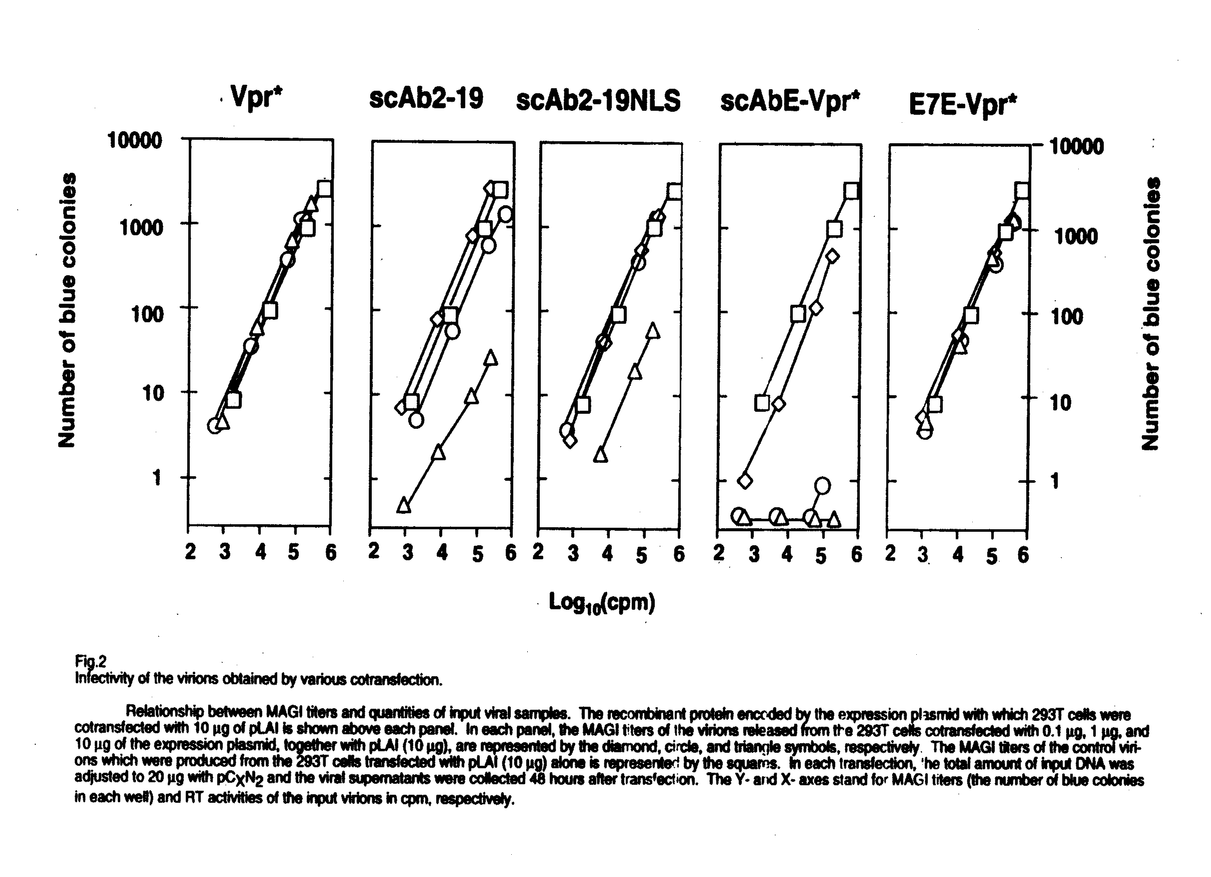  g of pLAI is shown above each panel. In each panel,the MAGI titers of the virions released from the 293T cells contransfected with 0.1 g of pLAI is shown above each panel. In each panel,the MAGI titers of the virions released from the 293T cells contransfected with 0.1 g,1 g,1 g,and 10 g,and 10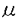 g of the expression plasmid,together with pLAI(10 g of the expression plasmid,together with pLAI(10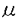 g),are represented by the diamond,circle,and triangle symbols,respectively.The MAGI titers of the control viri-ons which were produced from the 293T cells transfected with pLAI(10 g),are represented by the diamond,circle,and triangle symbols,respectively.The MAGI titers of the control viri-ons which were produced from the 293T cells transfected with pLAI(10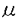 g)alone is representedby the squares.In each transfection,he total amout of input DNA was adjusted to 20 g)alone is representedby the squares.In each transfection,he total amout of input DNA was adjusted to 20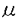 g with pCXN2and the viral supernatants were collected 48 hours after transfection.The Y-and X-axes stand for MAGI titers(the number of blue colonies in each well)and RT activities of the input virions in cpm,respectively. g with pCXN2and the viral supernatants were collected 48 hours after transfection.The Y-and X-axes stand for MAGI titers(the number of blue colonies in each well)and RT activities of the input virions in cpm,respectively.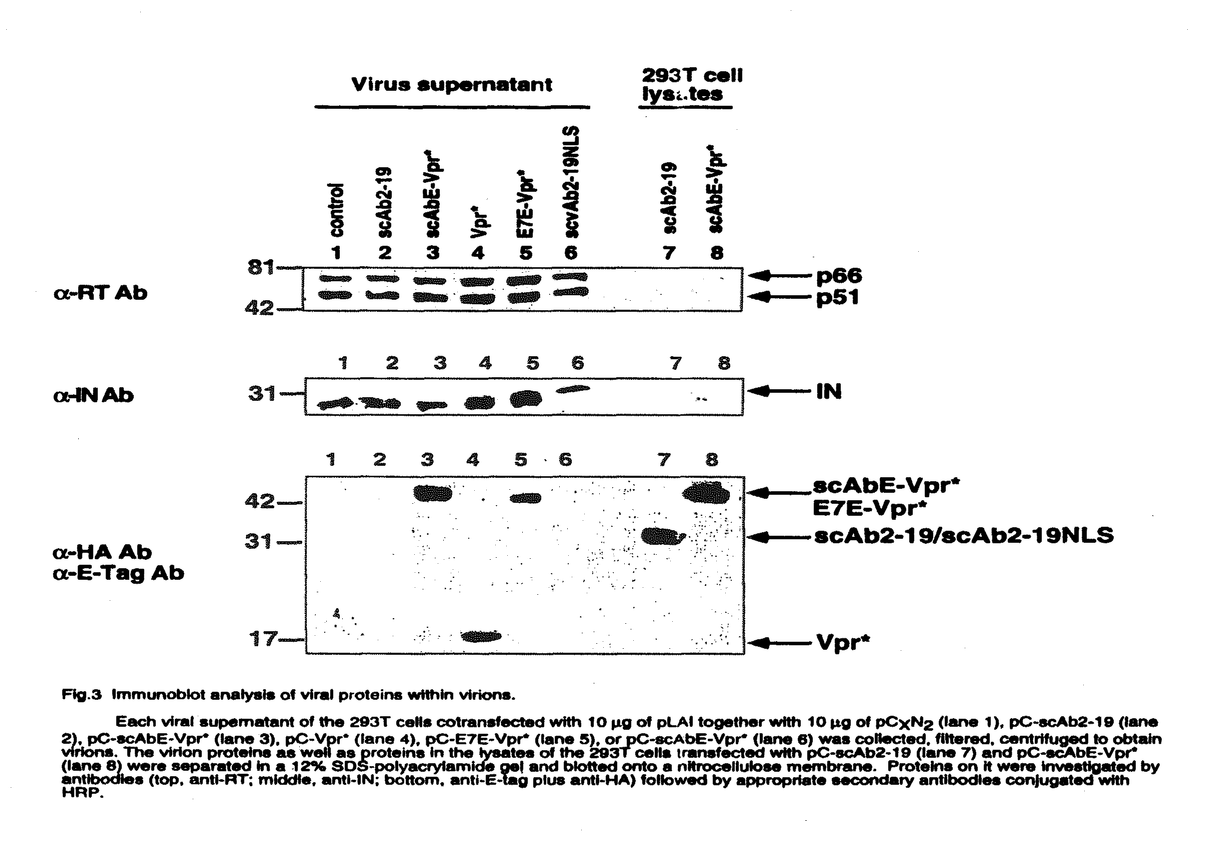  g of pLAI together with 10 g of pLAI together with 10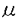 g of pCXN2(lane 1),pC-scAb2-19(lane 2),pC-scAbE-Vpr*(lane 3)pC-Vpr*(lane 4),pC-E7E-Vpr*(lane 5),or pC-scAbE-Vpr*(lane 6)was collected,filtered,centrifuged to obtain virions. The virion proteins as well as proteins in the lysates of the 293T cells transfected with pC-scAb2-19(lane 7)and pC-scAbE-Vpr*(lane 8)were separated in a 12%SDS-polyacrylamide gel and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane.Proteins on it were investigated by antibodies(top,anti-RT;middle,anti-IN;bottom,anti-E-tag plus anti-HA)followed by appropriate secondary antibodies conjugated with HRP. g of pCXN2(lane 1),pC-scAb2-19(lane 2),pC-scAbE-Vpr*(lane 3)pC-Vpr*(lane 4),pC-E7E-Vpr*(lane 5),or pC-scAbE-Vpr*(lane 6)was collected,filtered,centrifuged to obtain virions. The virion proteins as well as proteins in the lysates of the 293T cells transfected with pC-scAb2-19(lane 7)and pC-scAbE-Vpr*(lane 8)were separated in a 12%SDS-polyacrylamide gel and blotted onto a nitrocellulose membrane.Proteins on it were investigated by antibodies(top,anti-RT;middle,anti-IN;bottom,anti-E-tag plus anti-HA)followed by appropriate secondary antibodies conjugated with HRP. | |
| 審査要旨 | 本研究は、後天性免疫不全症候群の原因ウイルスである1型ヒト免疫不全ウイルス(HIV-1)の感染症に対する遺伝子治療に関するものである。本研究の遺伝子治療は、ウイルス粒子が細胞から出芽する際に抗ウイルス効果のある分子を取り込ませることによりウイルスの感染力を抑制させることを試みたものである。以下の結果を得ている。 1.抗ウイルス効果のある分子として、HIV-1インテグレース(HIVIN)に対する単鎖抗体(scAb2-19)とHIV-1のアクセサリー蛋白質であるVprとの融合蛋白質scAbE-Vpr*を作製した。単鎖抗体とは、IgGの可変領域を融合したポリペプチドである。 2.ニトロセルロース膜にHIVINを結合させ、scAbE-Vpr*またはscAb2-19を含む細胞抽出液でインキュベートし、それぞれに対する抗体を結合させて、scAbE-Vpr*およびscAb2-19のHIVINに対する結合能を評価した。これにより、scAbE-Vpr*が、HIVINと結合する能力が、scA2-19と同程度であることを示した。 3.Vpr、scAb2-19およびscAbE-Vpr*を発現するDNAとHIV-1 infectious clone pLAIをcotransfectionして、Vpr*-virus、scAb2-19-VirusおよびscAbE-Vpr*-virusを得た。これらのウイルスの産生量を、p24アッセイとRTアッセイで比較したところ、差は生じなかった。 4.上記のVpr*-virus、scAb2-19-virusおよびscAbE-Vpr*-virusの感染力をMAGIアッセイ法で比較した。scAbE-Vpr*-virusは、感染力が消失していた。scAb2-19-virusの感染力は、野生型ウイルスの100分の1であった。Vpr*-virusの感染力は、野生型ウイルスと同じであった。 5.Vpr*-virus、scAb2-19-virusおよびscAbE-Vpr*-virusの蛋白質をイムノブロットで確認した。Vpr*とscAbE-Vpr*は、ウイルス粒子に取り込まれていたが、scAb2-19は取り込まれていなかった。 6.Vpr*-virusおよびscAbE-Vpr*-virusをCEM細胞に感染させて、CEM細胞中のDNAを精製した。このDNAを元に、PCR法によりウイルスDNAを増殖させた。この結果、Vpr*-virusを感染させると直鎖状のウイルスDNAも環状のウイルスDNAも存在する。しかし、scAbE-Vpr*-virusを感染させた場合、直鎖状ウイルスDNAはあるが、環状ウイルスDNAはなかった。直鎖状ウイルスDNAがウイルス蛋白質とともに形成したpreintegration complex(PIC)が核移行すると環状ウイルスDNAができる。scAbE-Vpr*がHIVINに結合することによりPICの立体構造の変化やHIVINの機能を阻害して、PICの核移行を妨げていると予測された。 以上、本論文は、scAbE-Vpr*がウイルス粒子に取り込まれてウイルスの感染力をほぼ完全に消失させていることを明らかにした。scAbE-Vpr*を利用したHIV-1感染症に対する遺伝子治療の手法は、過去に考えられた出芽するウイルスに対する遺伝子治療戦略のなかでも、単鎖抗体を使用した点で新しく、非常に強い感染力抑制効果が得られた点で意義がある。本論文は、HIV-1感染症に対する遺伝子治療分野に重要な貢献をなすと考えられ、学位の授与に値するものと考えられる。 | |
| UTokyo Repositoryリンク | http://hdl.handle.net/2261/54078 |